Transformations in Matter and Energy Carbon TIME is an NSF-funded partnership led by Michigan State University
Lesson 4 - Explaining How Animals Move and Function
Students model and explain digestion, biosynthesis and cellular respiration using the Three Questions. They learn that the biomass of animals is mainly carbohydrates, fats, and proteins and relate the rearrangement of atoms in cellular respiration to energy release.
Guiding Question
How do animals use food to grow, move and function?
Activities in this Lesson
-
 Activity 4.1: Molecular Models for Cows Moving and Functioning: Cellular Respiration (40 min)
Activity 4.1: Molecular Models for Cows Moving and Functioning: Cellular Respiration (40 min) - Activity 4.2: Explaining How Cows Move and Function: Cellular Respiration (40 min)
Note: The steps that have students construct molecular models in this activity are optional if students did molecular modeling for cellular respiration in another unit and performed well on the pretest for items related to cellular respiration.
Unit Map
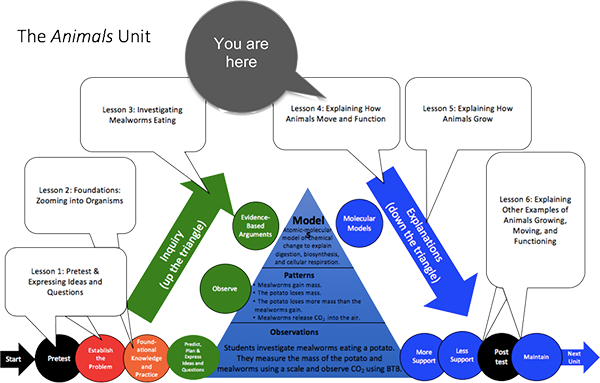
Target Performances
|
Lesson 4 –Explaining How Animals Move and Function |
|
|---|---|
|
Activity 4.1: Molecular Models for Cows Moving and Functioning: Cellular Respiration |
Students use molecular models to explain how carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen atoms are rearranged into new molecules in a cow’s cells. |
|
Activity 4.2: Explaining How Cows Move and Function: Cellular Respiration |
Students explain how matter moves and changes and how energy changes during cellular respiration in a cow’s cells (connecting macroscopic observations with atomic-molecular models and using the principles of conservation of matter and energy). |
NGSS Performance Expectations
Middle school
- MS. Matter and its Interactions. MS-PS1-1. Develop models to describe the atomic composition of simple molecules and extended structures.
- MS. Matter and its Interactions. MS-PS1-5. Develop and use a model to describe how the total number of atoms does not change in a chemical reaction and thus mass is conserved.
High school
- HS. Matter and its Interactions. HS-PS1-4. Develop a model to illustrate that the release or absorption of energy from a chemical reaction system depends upon the changes in total bond energy.
- HS. Matter and its Interactions. HS-PS1-7. Use mathematical representations to support the claim that atoms, and therefore mass, are conserved during a chemical reaction.
- HS. From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes. HS-LS1-7. Use a model to illustrate that cellular respiration is a chemical process whereby the bonds of food molecules and oxygen molecules are broken and the bonds in new compounds are formed resulting in a net transfer of energy.
- From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes. HS-LS1-2. Develop and use a model to illustrate the hierarchical organization of interacting systems that provide specific functions within multicellular organisms.
Talk and Writing
At this stage in the unit, the students will be developing Explanations. The table below shows specific talk and writing goals for this phase of the unit.
|
Talk and Writing Goals for the Explanations Phase |
Teacher Talk Strategies That Support This Goal |
Curriculum Components That Support This Goal |
|---|---|---|
|
Examine student ideas and correct them when there are problems. It’s ok to give the answers away during this phase! Help students practice using precise language to describe matter and energy. |
Let’s think about what you just said: air molecules. What are air molecules? Are you talking about matter or energy? Remember: atoms can’t be created. So that matter must have come from somewhere. Where did it come from? Let’s look at the molecule poster again… is carbon an atom or a molecule? |
Molecule Poster Three Questions Poster
|
|
Focus on making sure that explanations include multiple scales. |
The investigation gave us evidence for what was happening to matter and energy at a macroscopic sale. But what is happening at an atomic-molecular scale? What is happening to molecules and atoms? How does energy interact with atoms and molecules during chemical change? Why doesn’t the macroscopic investigation tell us the whole story? Let’s revisit our scale poster… what is happening to matter at the molecular scale? |
Molecular Models Molecular Modeling Worksheets Explanations Tool PPT Animation of chemical change Powers of Ten Poster |
|
Encourage students to recall the investigation. |
When did this chemical change happen during our investigation? How do we know that? What is our evidence? What were the macroscopic indicators that this chemical change took place? |
Evidence-Based Arguments Tool Investigation Video |
|
Elicit a range of student explanations. Press for details. Encourage students to examine, compare, and contrast their explanations with others’. |
Who can add to that explanation? What do you mean by _____? Say more. I think you said _____. Is that right? Who has a different explanation? How are those explanations similar/different? Who can rephrase ________’s explanation? |
Explanations Tool |

 Download PDF of Lesson 4 Teacher's Guide
Download PDF of Lesson 4 Teacher's Guide